This is part of our commercial offering.
If you are here, we assume that you have access to a Polyaxon EE Control Plane or Polyaxon Cloud.
Overview
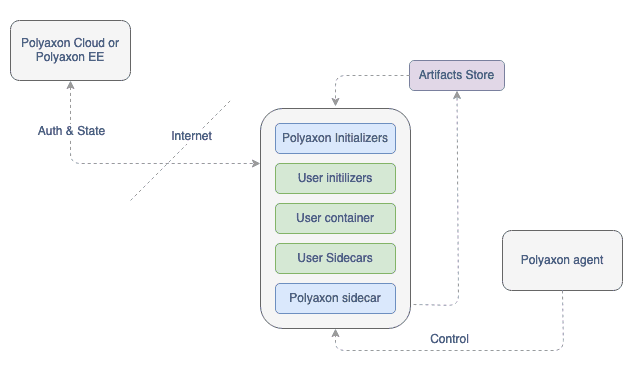
- Agents interact with Polyaxon Control Plane to check the queues that they manage for operations to start, stop, or update.
- Agents can deploy different artifacts store and connections to ensure isolation, it’s also possible to deploy similar configurations on different clusters to enable access to new resources, e.g. on-prem GPU and GKE for TPUs.
- Agents can be used to deploy jobs / distributed jobs workload, but they can also deploy and expose services.
It’s important to note that Polyaxon Agent is an important piece in Polyaxon’s architecture to enable complete isolation of workload and artifacts and a hybrid execution and management of resources.
Create a namespace for the agent
Agents are deployed and use a namespace to run operations independently of other applications running on your cluster.
kubectl create namespace polyaxon
# namespace "polyaxon" createdIf you would like to use a different value, you must keep in mind to update the namespace value in your config.
Configuration
This section will help you create a configuration file to deploy an agent. Polyaxon Agent ships with default values, however and depending on your use case you may need to override some of these values. To do so, you need to create a configuration file and we recommend to save it somewhere safe so that you can reuse it in the future.
Create a config file config.yaml or polyaxon_config.yaml,
and set up all information you want to override in the default config.
If you are using Polyaxon CLI to deploy Polyaxon, we suggest that you define the version and deployment type:
deploymentChart: agent
deploymentVersion: 1.1.0In Polyaxon UI you can get an starter deployment config:
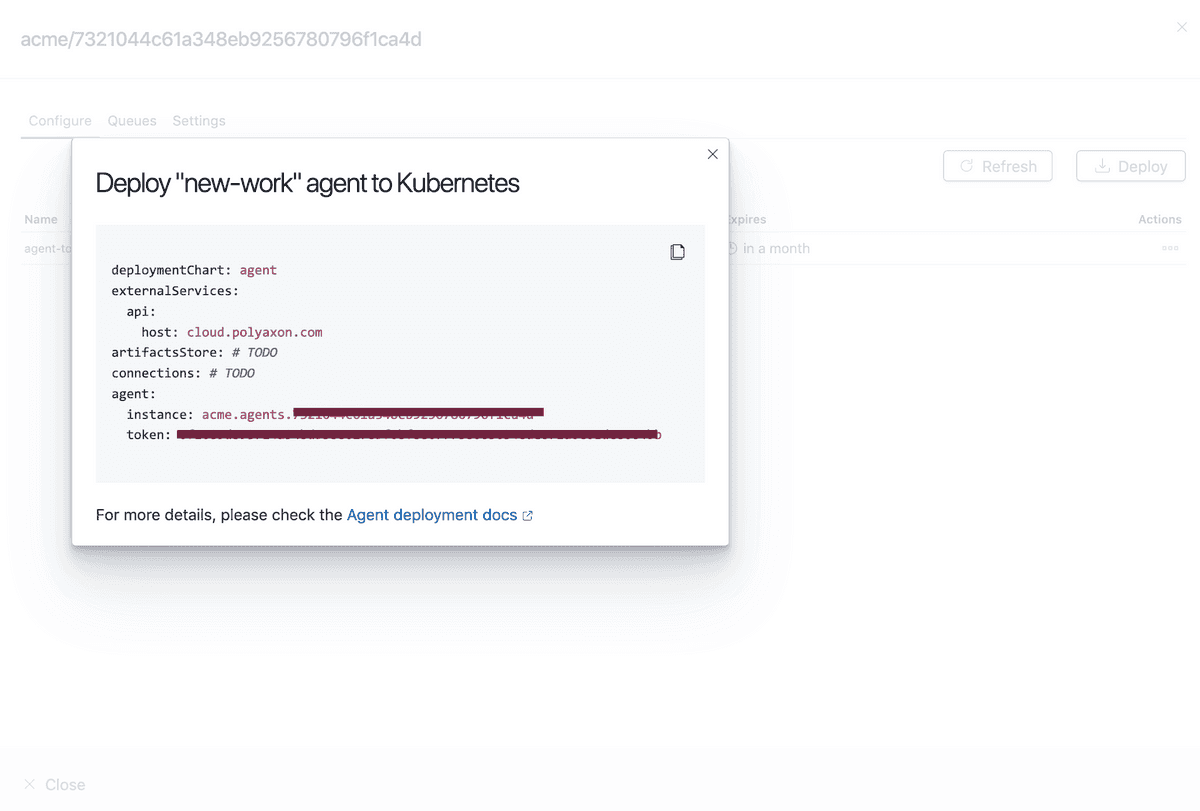
To manage agents please check the management section
Install Polyaxon Agent
First of all, you need to add the Polyaxon helm repository to your Helm, so you can install Polyaxon from it. This makes it easy to refer to the Polyaxon chart without having to use a long URL each time.
helm repo add polyaxon https://charts.polyaxon.com
helm repo updateValidate
You can validate that your deployment config.yaml file is compatible with the version you are trying to deploy:
polyaxon admin deploy -f config.yaml --checkDry run
To perform a dry run:
polyaxon admin deploy -f config.yaml --dry-runDeploy
Now you can install Polyaxon Agent with your config.yaml file.
Note: it’s important to know that there’s an initial delay before you can access Polyaxon API, and before some pods will turn green, which is set to 2 minutes.
You can use Polyaxon CLI to manage the deployment
polyaxon admin deploy -f config.yamlOr you can use Helm to do the same:
in Helm 2
helm install polyaxon/agent \
--name=<RELEASE_NAME> \
--namespace=<NAMESPACE> \
-f config.yamlin Helm 3
helm install <RELEASE_NAME> polyaxon/agent \
--namespace=<NAMESPACE> \
-f config.yaml--name or name is an identifier used by helm to refer to this deployment.
You need it when you are changing the configuration of this install or deleting it.
We recommend using RELEASE_NAME = polyaxon or RELEASE_NAME = plx.
--namespace should be the same value of the namespace you created in the first step,
we again recommend using polyaxon to make it always easy to remember.
Tip: We recommend using
polyaxonfor both the--nameand--namespaceto avoid too much confusion. The same command withpolyaxonas a value:
helm install polyaxon/agent \
--name=polyaxon \
--namespace=polyaxon \
-f config.yamlNote: “Release name already exists error” If you get a release named
<RELEASE_NAME>already exists error, then you should delete the release by runninghelm delete --purge <RELEASE_NAME>.
You can see the pods being created by entering in a different terminal:
kubectl --namespace=<NAMESPACE> get podWhen helm is done deploying Polyaxon, it will output some instructions NOTES,
these note will be different depending on your configuration (the service type used and/or ingress);
NOTES: ...These notes are important for setting the CLI, and getting access to the dashboard.
Next step you need the Polyaxon CLI installed, and you need to configure the host and the ports based on these notes.
Upgrade Polyaxon Agent
To upgrade Polyaxon to a newer version, you can simply run the following command using Polyaxon CLI:
polyaxon admin upgrade -f config.yamlOr using Helm
helm upgrade polyaxon polyaxon/agent -f config.yamlTurn off a Polyaxon Agent
When you are done with an agent, you can turn off the deployment, and depending on your persistence configuration you can keep all your data saved for future deployments.
You can also decide to completely turn off Polyaxon and remove the namespace and computational resources.
polyaxon admin teardown -f config.yaml
Or
helm del --purge polyaxon
You can also delete the agent from the dashboard.
Delete the namespace
Delete the namespace the agent was installed in. This deletes any disks that may have been created to store user’s logs, and any IP addresses that may have been provisioned.
kubectl delete namespace <your-namespace>If you used the default values, the command should be,
kubectl delete namespace polyaxon