Core Architecture
Polyaxon is structured as a modern, decoupled, micro-service oriented architecture.
- A robust core JSON API
- An Asynchronous, customizable, and scalable scheduler
- An extensive tracking API
- An event/action oriented interface
- A pipeline engine capable of authoring workflows as directed acyclic graphs (DAGs)
- An optimization engine to search automatically and concurrently for the best hyperparameters in a search space based on state of the art algorithms
- A CI system to trigger experiments/hyperparameter tuning/pipelines automatically based on some event and track their execution and report results to users
These components work together to make every Polyaxon deployment function smoothly, but because they’re decoupled there’s plenty of room for customization.
In fact, users can decide for example to deploy only the core and using an external tracking service, or replace the built-in scheduler, pipeline, and optimization engine with other platforms.
How things fit together
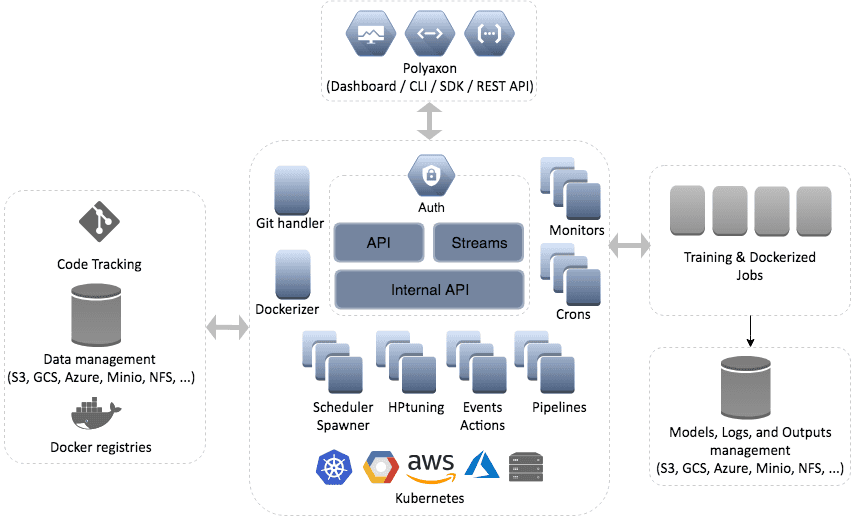
Polyaxon relies on several components to function smoothly:
- Postgres database
- redis
- rabbitmq
- connections: docker registries, artifacts stores, git connections, …
Polyaxon schedules your workload to Kubernetes, so you will need:
- Kubernetes cluster(s) for deploying one or several Polyaxon Agents
Polyaxon platform
In order to understand how Polyaxon can help you organize your workflow, you need to understand how Polyaxon abstract the best practices of data science job.
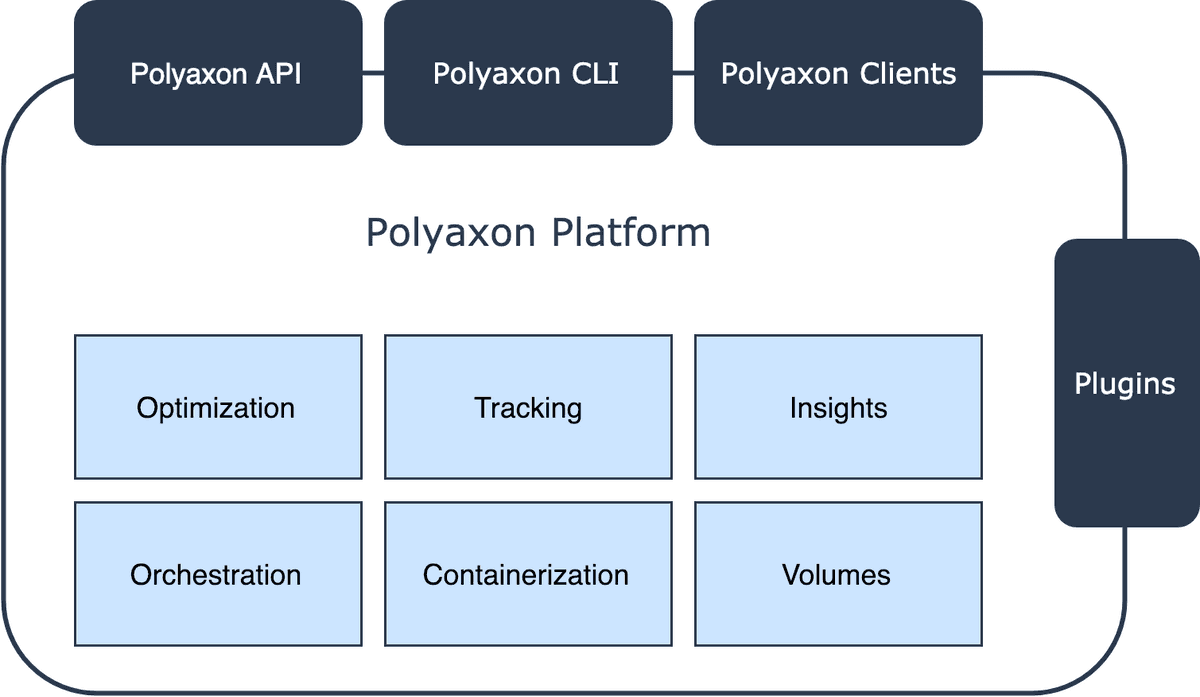
Polyaxon runs both in the cloud and on-premise, and provides access via:
- Polyaxon command line interface
- Polyaxon dashboard
- Polyaxon SDKs targeting the Polyaxon API
- Polyaxon Webhooks
These interfaces hide the powerful abstractions provided by the Polyaxon architecture. When a machine learning engineer or a data scientist schedules a job or an experiment, Polyaxon relies on Kubernetes for:
- Managing the resources of your cluster (Memory, CPU, GPU, TPU, …)
- Creating easy, repeatable, portable deployments
- Scaling up and down as needed
Polyaxon does the heavy lifting of:
- Exposing a rich runtime including jobs, services, distributed jobs
- Scheduling operations
- Automation with a flow engine and an optimization engine
- Resolving dependencies between operations
- Validating and authorizing access to resources, connections, namespaces
- Creating docker images
- Monitoring the statuses and resources
- Streaming logs
- Tracking code version, params, logs, configurations, and tags
- Reporting metrics and outputs and other results to the user
- Driving insights, knowledge, and analytics about your experiments
- Exposing a rich workspace based on Notebooks, Streamlit, VSCode, …